Elemental analysis: Precise determination of elemental concentrations
Elemental analysis is an analytical method used to determine the elemental composition of a sample. It provides precise information about the elements of the non-metals carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) and sulfur (S), as well as phosphorus (P) and halogens contained in organic and inorganic materials. These elements are considered the basic elements of living nature. Accordingly, their elemental composition is of crucial importance in numerous applications, including chemistry and materials science, environmental analysis, food chemistry, pharmaceutical research and quality control.
Do you want to know more about the history of elemental analysis?
Our book "125 Years of Instrumental Elemental Analysis - A success story" offers you deep insights into the development of elemental analysis from the very first beginning up to latest trends nowadays. Which pioneers have laid the foundation for elemental analysis with their innovative ideas and research? How has elemental analysis developed from the early stage to an industrial produced technology? What is the technological platform that the method is based on and which applications can be covered? Which role have we as Elementar played in the development of elemental analysis? All these questions are getting answered in the book. Enjoy reading.

DOWNLOAD YOUR COPY
Fill in the form to receive your download link per e-mail.
Your contractual consideration for the free provision of the download is the subscription to our personalized newsletter. By clicking on the “download now” button, you therefore declare your acceptance of the receipt of personalized newsletters by e-mail by Elementar India Pvt Limited and its group companies as well as the evaluation of your user behavior in this regard and - if available - the merging of this data with your data in our customer database.
In order to receive newsletters from our group companies it is necessary to transfer your above-mentioned personal data to these companies. The data transfer is contractually required.
You are aware that the subscription to our personalized newsletter represents the contractual consideration that you provide for the free provision of the download. You can unsubscribe from the newsletter at any time with effect for the future. You can object to the future use of your data for advertising purposes at any time. For further information, please refer to our privacy policy.
Qualitative vs. quantitative elemental analysis
Quantitative elemental analysis
The quantitative elemental analysis determines the amount of each individual element in the sample. The result is typically expressed as a mass percentage (e.g. %C, %H, %N) or as an atomic ratio. Among other things, quantitative analysis is crucial for the quality control of a wide range of starting and end products, the determination of the purity of substances, the control and cultivation of food and animal feed, the protection of our environment and the generation and supply of energy.
Qualitative elemental analysis
In contrast, qualitative elemental analysis only identifies which elements are present in the sample without determining their exact quantity. It is often used as a preparatory step for quantitative analysis or for the rapid identification of elements in unknown samples. Methods such as X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF) can be used for qualitative purposes.
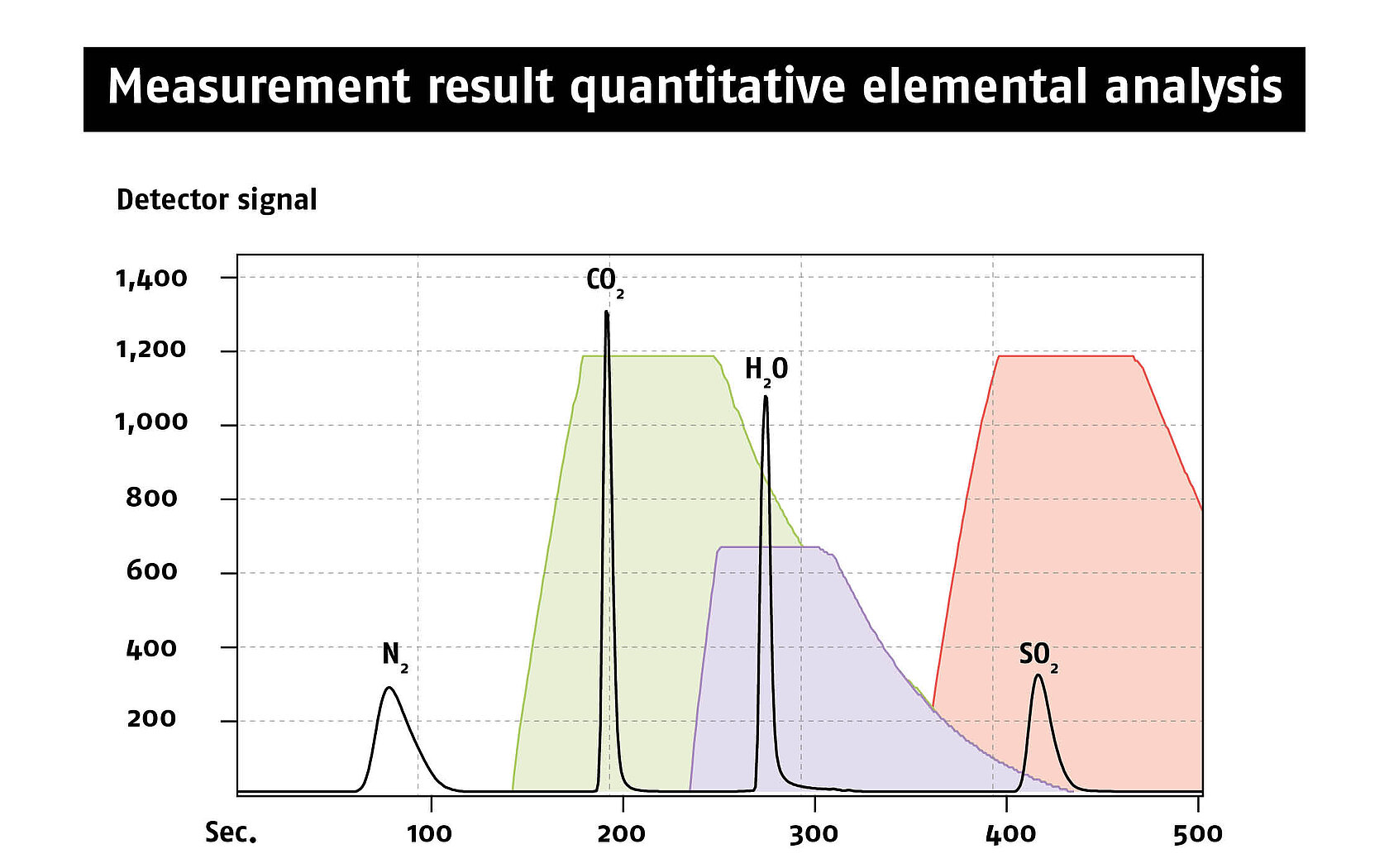
Perfect gas separation and sharp signals are the hallmarks of our Advanced Purge and Trap (APT) technology. This results in the best determination limits and large measuring ranges.
Precise CHNOS analysis thanks to organic elemental analysis
Organic elemental analysis focuses on the determination of the elemental composition of organic compounds, which typically contain CHNOS, sometimes also phosphorus and halogens. Organic elemental analysis is one of the most exact and precise technologies in the world of analytical science for determination of the main components of a sample. A state-of-the-art instrument can determine the content of an element at the lower PPM level with 100 % accuracy without a need for special calibration. Optimized analyzers can enable determination limits up to the lower ppb level. Regardless of the sample matrix, the same procedure can analyze completely different types of samples.
A distinction is made between organic elemental analysis and elemental analysis. Organic elemental analysis involves the determination of CHNOS in organic samples such as soil, pharmaceuticals and fuels, but also inorganic materials such as metals, ceramics or minerals. Elemental analysis deals with the determination of a selection of elements from the entirety of chemical elements (from boron to uranium).
State-of-the-art: elemental analysis using combustion analysis
The current state-of-the-art for CHNS analysis is combustion analysis. This involves combusting the sample to convert the elements it contains into measurable, gaseous compounds. In addition to combustion analysis, there are other ways of breaking down the sample, e.g. using high-temperature pyrolysis to precisely analyze the oxygen content. The resulting gases are then quantified, typically using detectors such as thermal conductivity detectors (TCD) or infrared detectors (IR).
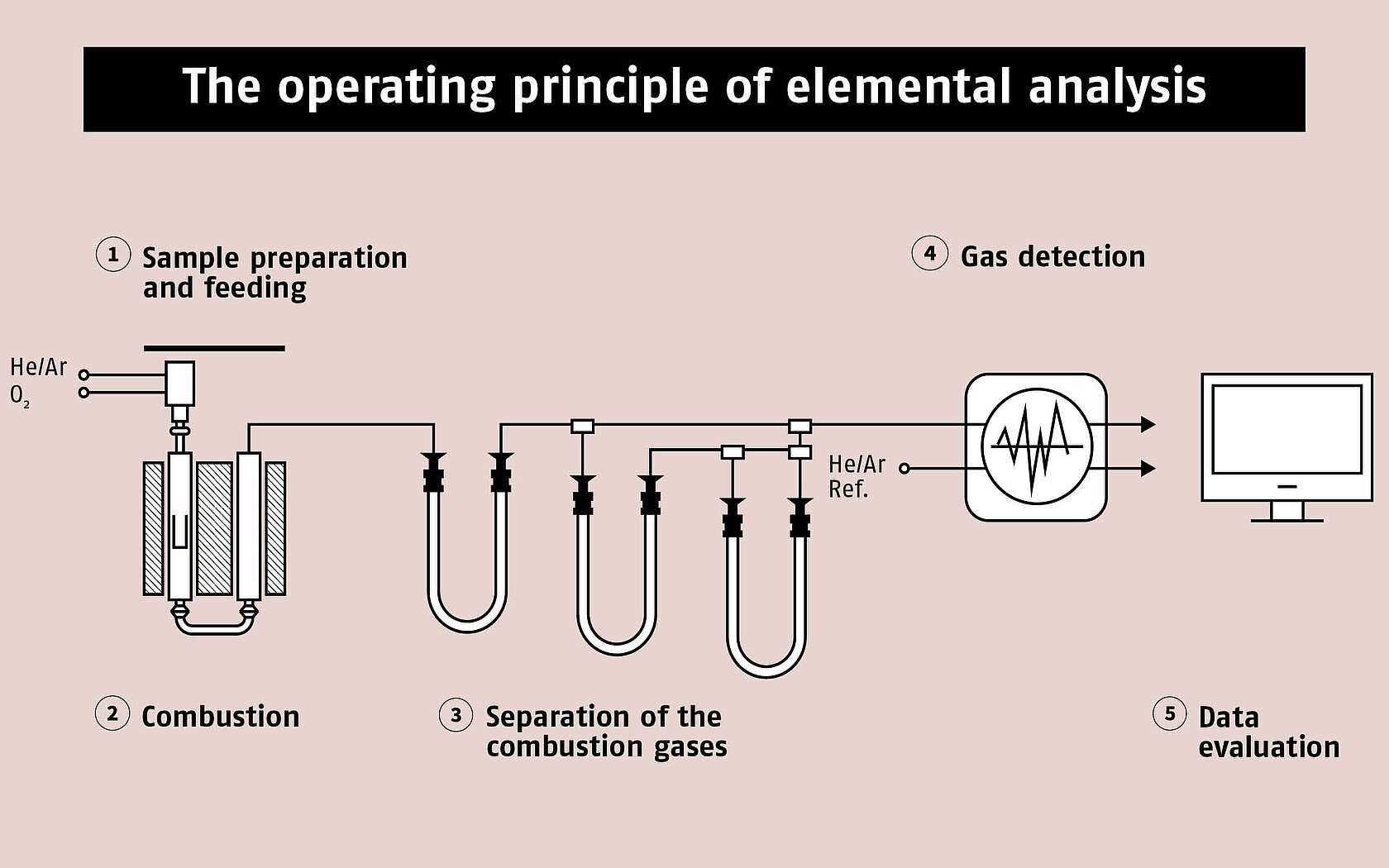
1. Sample preparation and feeding
Depending on the type of sample and physical state, the sample is weighed in tinfoil, a crucible, or a capsule and placed on an autosampler. The autosampler can be equipped with up to 120 positions to allow 24/7 operations with the highest level of sample throughput. The sample should be introduced in the absence of ambient air and without pressure surges to avoid falsifying the result.
2. Combustion
The goal is to destroy the molecular structure of the sample completely. This is where the designation combustion analysis comes from. Combustion occurs in an ash finger at the hottest point in the combustion tube. A precisely dosed oxygen supply that is adapted to the sample is crucial for the intelligent control of the combustion.
3. Separation of the combustion gases
The gas mixture that streams from the combustion tube consists of sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen. Except for the latter, each gas is specifically and quantitatively reversibly adsorbed in the downstream chromatography columns.
4. Gas detection
The detector successively measures all the combustion gases so that all of them can be determined uniquely and quantitatively. The signal intensity correlates directly with the amount of the respective element in the original sample.
5. Computer-aided data evaluation
The elemental analyzer is operated and controlled by a computer using the instrument software. The elemental composition of the sample is calculated based on the measured values and indicated in the software in the form of mass percentages or atomic ratios.
Application examples of elemental analysis
Industry, governmental agencies, universities, and research institutes are the primary users of the instruments. In those places they create facts and thus have become an indispensable aid in a variety of industries, sectors, scientific disciplines, and fields of work. At their core, the technologies foster the quality of products and support a sustainable approach to our environment. At the same time, they have the potential to drive research and trigger new developments.
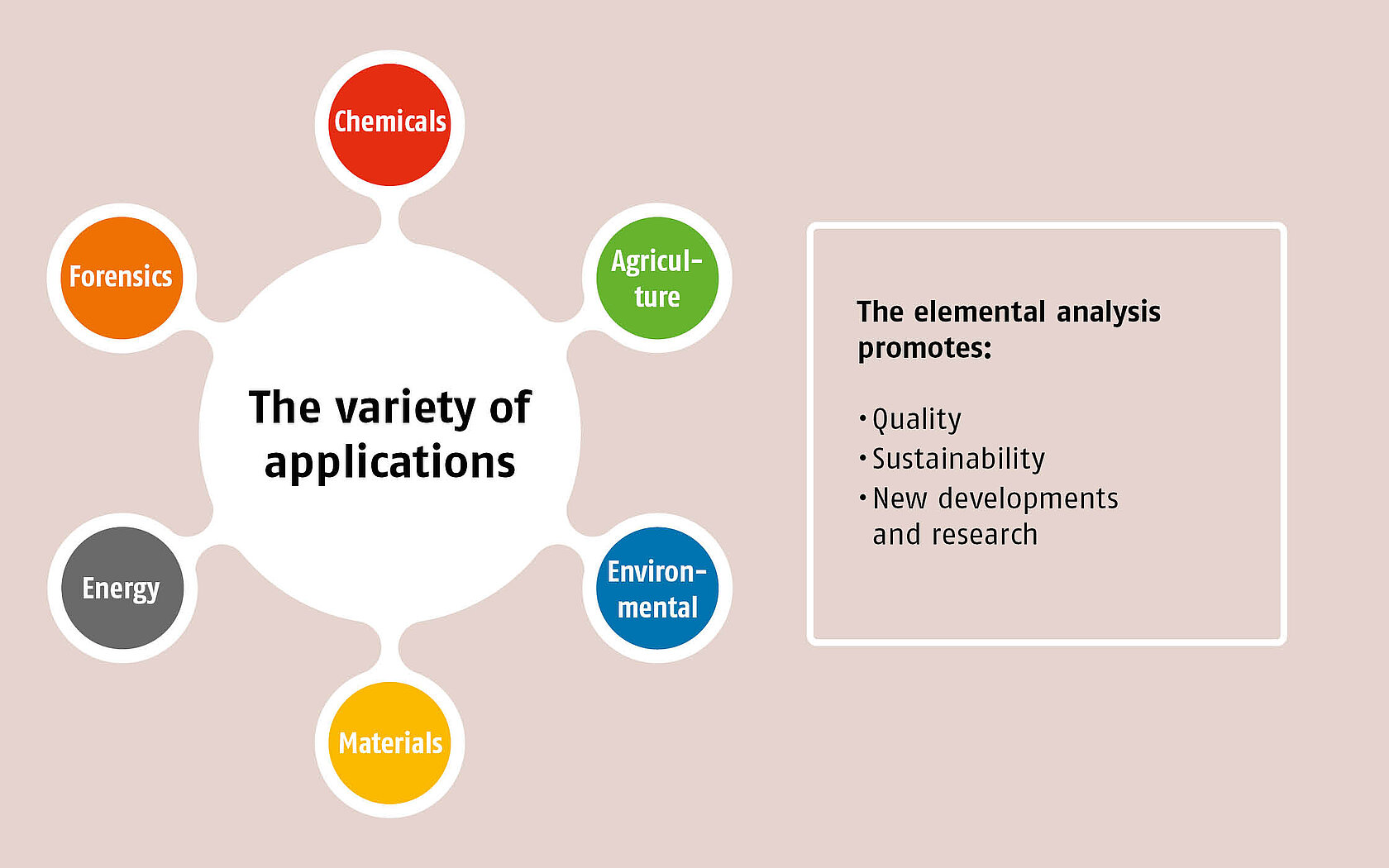
Selected application examples
CHNS analysis in pharmaceutical products
The concentrations of CHNS and O in pharmaceutical products can serve as important parameters for controlling the production process. For example, the concentration of an active ingredient with a certain elemental composition, which is mixed into a carrier material with a different elemental composition, can be easily and cost-effectively detected by CHNS elemental analysis. Further information: GMP Guide: Ready for the audit
CHN analysis in coal
CHN elemental analysis of coal is one of the standard methods for determining the quality of solid fossil fuels. Ideally, high sample weights are analyzed, as the samples are normally inhomogeneous and the result of the CHN analysis is therefore more meaningful and comparable. Further information: CHN analysis in coal and fly ash

CNS analysis in plant material

CNS analyses in plant material place high demands on the simultaneous measurement of very low S contents in addition to high C contents. Furthermore, high sample weights are ideally analyzed for this purpose, as the plant materials are often inhomogeneous. Further information: CNS analysis in in plant material
CN analysis in soil
CN analysis is used to obtain information on soil fertility. The carbon and nitrogen content (C/N ratio) of the soil is directly related to its ability to support healthy plant growth. Further information: CN analysis in soil

CS analysis in steel

The carbon and sulfur content significantly influences the mechanical properties of steel, e.g. how ductile (malleable) or corrosion-resistant it is. Accordingly, quality control by means of CS analysis is essential to ensure that the steel has the required properties. Further information: CS analysis in steels
Advantages of elemental analysis
Elemental analysis represents the oldest industrially developed analysis technology. It was an indispensable tool for the founders of organic chemistry. It essentially made the great chemical syntheses of the nineteenth century possible. Based on its technical maturity, it functions in an analytical laboratory as the last instance for the quantitative determination of elements C, H, N, O, and S in organic samples to this very day.
Elemental analysis is the workhorse of a chemical laboratory: It runs and runs and runs. The method is robust, fast, and simple, especially in terms of the preparation of samples. It makes the combustion analysis ever more interesting for many new application areas. It also has a potential to replace obsolete technologies that require environmentally harmful chemicals. The high degree of automation that the technology possesses means that it is highly efficient.
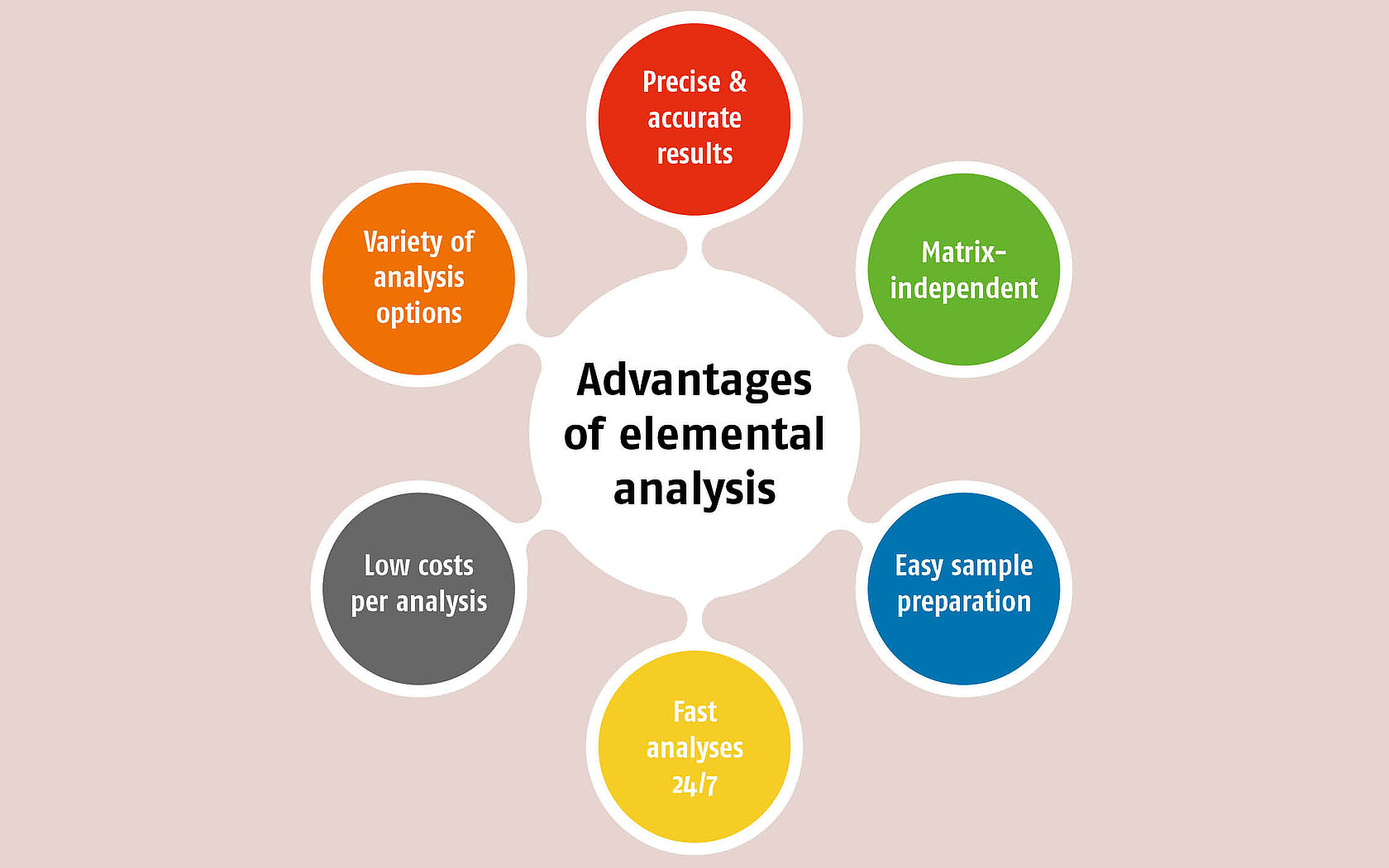
Advantages in detail
- The methods of elemental analysis are primarily characterized by impressive precision and accuracy. Even traces of elements can be revealed with certitude regardless of the high content of other elements, such as carbon.
- Elemental analysis is something of an absolute method. It measures and determines the quantities of elements directly. Unlike spectroscopic analysis methods, it does not require any validation.
- The elements are determined independently of the matrix: No matrix-specific standards are required. The instrument is calibrated with ultrapure fine chemicals.
- No extensive preparation of the sample is required. The sample does not need to be extracted or wet-chemically digested into any form.
- The determination process is quick and simple. All measurements can be operated fully automated 24/7. The four elements C, H, N, and S can be determined within 10 minutes.
- Compared with other analytical methods, the costs for each analysis are low, and the investment in an instrument amortizes itself rapidly.
- No toxic residues are created. Organic toxins are disposed of thermically.
- Elemental analysis allows a variety of analysis options.
Our solutions for elemental analysis
We offer advanced elemental analyzers that are characterized by precision, reliability and ease of use. Our instruments are suitable for a wide range of applications and sample materials and enable precise CHNOS elemental analysis.
Get in touch with us
Do you have questions about combustion analysis or are you interested in carrying out elemental analysis yourself? Our team will be happy to answer your questions about our services, analyzers and the applications that you can cover with our solutions. Get in touch with us and let us know how we can support you.
If you would like to receive our newsletter, by clicking on the “Submit” button you consent to receiving personalized newsletters by email from Elementar India Pvt Ltd and its group companies, as well as to the evaluation of my user behavior in this regard and – if available – the merging of this data with my data in our customer database.
In order to receive newsletters from our group companies, it is necessary to transmit the above-mentioned data to them. The data transfer to these recipients is legitimized by your consent, which you give by clicking on the “Submit” button.
The newsletter can be canceled at any time with effect for the future as well as my consent to the transfer to our group companies can be revoked at any time. A revocation does not affect the legality of the processing carried out on the basis of the consent until the revocation. For more information, please refer to our privacy policy.

